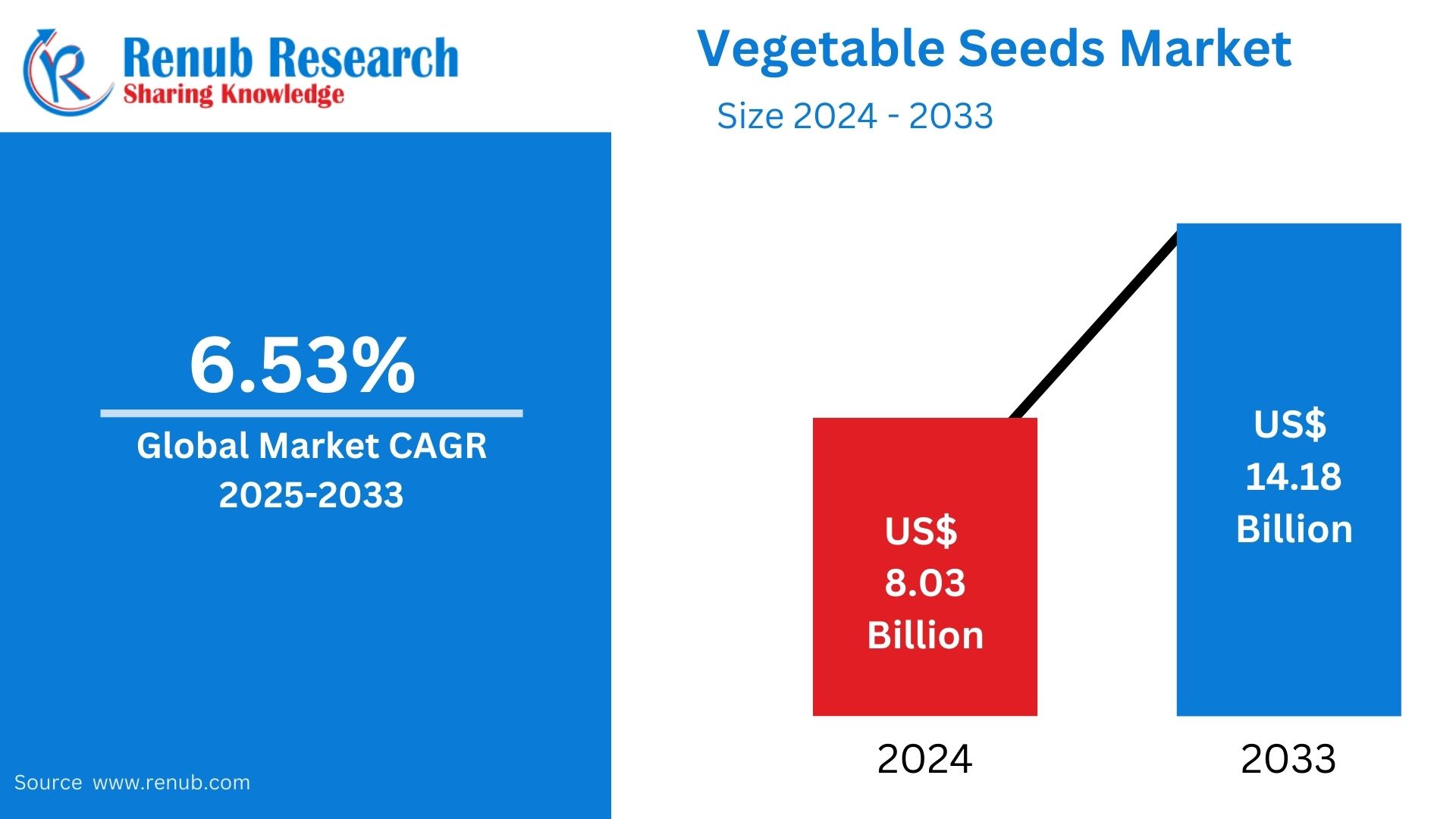
The global vegetable seeds market, valued at US$ 8.03 billion in 2024, is entering a period of accelerated transformation. According to Renub Research, the market is expected to reach US$ 14.18 billion by 2033, expanding at a CAGR of 6.53% during 2025–2033. This robust trajectory reflects a shift toward high-quality hybrid seeds, increased adoption of biotechnology, and growing consumer preference for organic, non-GMO produce.
As nations grapple with food security, climate resilience, and sustainable agriculture, vegetable seeds—small but powerful components of the global food chain—have never been more important. Their role stretches far beyond simple crop production: they influence yields, disease resistance, nutritional value, and ultimately the stability of the global food system.
Request Free Sample Report
Vegetable Seeds: Foundation of Modern Agriculture
Vegetable seeds represent the reproductive units of vegetable crops, enabling the cultivation of tomatoes, cucumbers, carrots, peppers, leafy greens, and root vegetables across ecosystems worldwide. These seeds are available primarily in three forms:
Hybrid seeds – cultivated for high yield, pest resistance, and uniformity
Open-pollinated varieties (OPVs) – valued for seed-saving and biodiversity
Genetically modified (GM) seeds – engineered for resilience and productivity
Farmers today make seed choices based on soil health, climatic suitability, availability of irrigation, and expected yield performance. Hybrid seeds dominate commercial agriculture due to their ability to deliver consistency, high yields, and resilience against pests and diseases. In contrast, organic growers lean toward OPVs and non-GMO seeds in response to consumer demand for chemical-free and sustainable farming.
As global populations rise and consumer diets evolve, demand for both fresh and processed vegetables is increasing rapidly. This pushes the vegetable seed industry to innovate and supply cultivars that can perform reliably under unpredictable climatic and economic conditions.
Key Market Drivers Fueling Growth
1. Surging Demand for High-Yielding, Disease-Resistant Crops
With the global population projected to exceed 9.7 billion by 2050, nations face unprecedented pressure to scale up food production. Hybrid vegetable seeds have become indispensable for achieving higher yields and reducing crop losses. Their resistance to pathogens, pests, and environmental stressors significantly reduces both waste and input costs.
In April 2023, the University of California introduced five new strawberry varieties that offer high yields and strong soilborne disease resistance—a clear indication of global momentum in seed innovation. As urbanization expands, the need for reliable, high-performing seeds to sustain food supply chains is becoming a strategic priority worldwide.
2. Biotechnology Transforming Seed Production
Biotechnological advancements—particularly genetic modification, CRISPR gene editing, and molecular breeding—are reshaping the vegetable seeds landscape. These technologies enhance:
Drought and heat tolerance
Nutritional density
Resistance to pathogens
Shelf-life and uniformity
Improved seed treatment and coating technologies also enhance germination rates, storage life, and protection from soil-based diseases.
In September 2024, India showcased the power of agricultural biotech by releasing 109 new seed varieties developed by ICAR, each designed to boost productivity, climate resilience, and food security. Such government-backed breakthroughs are expected to amplify adoption across Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
3. Rapid Expansion of Organic and Non-GMO Farming
Organic farming is no longer a niche. By 2022, organic cultivation reached 96+ million hectares globally, increasing more than 20 million hectares in a single year.
This shift encourages farmers to purchase:
Non-GMO seeds
Open-pollinated varieties
Organic-certified seeds
Governments around the world have begun incentivizing organic farming through subsidies, training programs, and awareness campaigns, fueling demand for naturally bred vegetable seeds.
Consumers are becoming more health-focused, and the post-pandemic era has accelerated demand for sustainable, traceable, chemical-free produce—a trend expected to power the vegetable seeds market throughout the forecast period.
Challenges Restraining Market Growth
1. High Cost of Hybrid and Genetically Modified Seeds
Despite their high performance, hybrid and GM seeds remain expensive, particularly for smallholder farmers in developing countries. These seeds often require:
Greater irrigation
Higher fertilizer inputs
Specialized cultivation practices
Such dependencies raise total production costs. Without sufficient subsidies or credit access, many farmers continue relying on cheaper, traditional seeds—creating productivity gaps across regions.
2. Regulatory and Environmental Challenges
GM seeds face strict regulatory scrutiny worldwide. Lengthy approval processes delay commercialization and inflate R&D expenses. Public resistance surrounding GM crops—related to biodiversity concerns and possible cross-contamination—poses an additional barrier.
In regions with stringent GMO regulations, seed companies struggle to introduce advanced varieties, slowing market penetration and technological adoption.
Country-Level Market Insights
Canada: Strong Push Toward Sustainable, High-Tech Agriculture
Canada’s vegetable seeds market is benefitting from:
Rising demand for local, sustainable produce
Adoption of disease-resistant hybrid seeds
Rapid expansion of greenhouse farming
In August 2024, Syngenta announced its largest NK Seeds corn portfolio in over a decade, introducing eight new hybrids for the 2025 season. Backed by an annual US$ 1.4 billion R&D investment and 6,500 global employees, the company’s innovation pipeline continues to influence seed quality across North America.
Denmark: Europe’s Leader in Organic and Eco-Friendly Seed Use
Denmark’s agricultural policies aggressively promote organic farming and discourage GM use. Farmers prioritize:
OPVs
Organic-certified seeds
High-quality hybrids aligned with environmental standards
In 2024, the government expanded its innovative “Særpuljer” (Special Pools) program, aimed at supporting climate-friendly food production, biosolutions, and waste reduction. With consumers favoring local, chemical-free vegetables, Denmark remains a leading European market for sustainable seed development.
China: A Global Powerhouse in Vegetable Production
China’s immense population and massive vegetable consumption make it one of the world’s largest vegetable seeds markets. Hybrid seeds dominate due to their superior yields and adaptability across China’s varied agroclimatic zones.
China is a global leader in precision farming, genetic research, and seed breeding technologies. Government subsidies and modernization policies support widespread adoption of improved seeds.
In 2022, China cultivated vegetables on 22.7 million hectares, a 3.9% increase from 2017. Rising incomes, the push for food safety, and demand for organic vegetables further strengthen market expansion.
Brazil: Vast Farmland Meets Rising Demand for Vegetable Diversity
Brazil’s dynamic vegetable seeds market benefits from:
Favorable growing conditions
Rising consumption of fresh and processed vegetables
Expanded use of hybrid seeds for enhanced yields
In 2024–2025, the Brazilian government approved a record R$ 475.5 billion (US$ 88.2 billion) under its Crop Plan—marking the country’s largest agricultural credit program ever. This funding supports advanced farming technologies, sustainable practices, and supply chain upgrades, making Brazil a growing force in the global vegetable seeds industry.
Market Segmentation
By Type
Open-Pollinated Varieties (OPVs)
Hybrid Seeds
By Crop Type
Solanaceae (tomato, pepper, eggplant)
Root & Bulb (carrot, onion, garlic)
Cucurbit (cucumber, melon, squash)
Brassica (cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli)
Leafy (spinach, lettuce)
Others
By Cultivation Method
Protected (Greenhouse/Controlled Environment)
Open Field Cultivation
Regional Outlook
North America: United States, Canada
Europe: France, Germany, Italy, Spain, U.K., Belgium, Netherlands, Turkey
Asia Pacific: China, Japan, India, South Korea, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, Australia, New Zealand
Latin America: Brazil, Mexico, Argentina
Middle East & Africa: Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa
Each region shows unique growth patterns influenced by technology adoption, climatic constraints, government policies, and consumer preferences.
Key Companies Covered (with 3 Viewpoints Each)
BASF A.G.
Syngenta AG
Groupe Limagrain
Bayer AG
Sakata Seeds Corporation
UPL Ltd.
Gansu Dunhuang Seeds Co., Ltd.
JK Agri Genetics Ltd.
These companies dominate through hybrid innovation, global distribution networks, and investments in biotechnology and sustainable agriculture.
Final Thoughts
The global vegetable seeds market is evolving rapidly, underpinned by rising food demand, technological innovation, and the global shift toward organic and climate-smart agriculture. As the market grows from US$ 8.03 billion (2024) to US$ 14.18 billion by 2033, it is clear that high-quality seeds will form the cornerstone of the future food system.
With accelerating adoption of hybrid seeds, gene-edited varieties, and sustainable cultivation practices, the vegetable seeds industry is poised to play a pivotal role in strengthening global food security while addressing the challenges of climate change and population growth.